- Welcome to the Docs
- Get Docker
- Get Started
- Docker ID
- Docker Engine
- User Guide
- Introduction
- Work with images
- Docker storage drivers
- Network configuration
- Apply custom metadata
- Admin Guide
- Configuring and running Docker
- Automatically start containers
- Limit a container's resources
- Keep containers alive during daemon downtime
- Control and configure Docker with systemd
- Format command and log output
- Run a local registry mirror
- Logging
- PowerShell DSC Usage
- Using Ansible
- Using Chef
- Using Puppet
- Using Supervisor with Docker
- Runtime metrics
- Link via an ambassador container
- Troubleshoot Docker Engine
- Manage a swarm
- Swarm mode overview
- Swarm mode key concepts
- Get started with swarm mode
- How swarm mode works
- Run Docker Engine in swarm mode
- Join nodes to a swarm
- Manage nodes in a swarm
- Deploy services to a swarm
- Manage sensitive data with Docker secrets
- Lock your swarm
- Attach services to an overlay network
- Swarm administration guide
- Raft consensus in swarm mode
- Secure Engine
- Extend Engine
- Dockerize an application
- Dockerfile reference
- Docker run reference
- Use the Docker command line
- Daemon CLI reference (dockerd)
- Engine CLI reference
- docker (base command)
- docker attach
- docker build
- docker checkpoint *
- docker commit
- docker container *
- docker container
- docker container attach
- docker container commit
- docker container cp
- docker container create
- docker container diff
- docker container exec
- docker container export
- docker container inspect
- docker container kill
- docker container logs
- docker container ls
- docker container pause
- docker container port
- docker container prune
- docker container rename
- docker container restart
- docker container rm
- docker container run
- docker container start
- docker container stats
- docker container stop
- docker container top
- docker container unpause
- docker container update
- docker container wait
- docker cp
- docker create
- docker deploy
- docker diff
- docker events
- docker exec
- docker export
- docker history
- docker image *
- docker images
- docker import
- docker info
- docker inspect
- docker kill
- docker load
- docker login
- docker logout
- docker logs
- docker network *
- docker node *
- docker pause
- docker plugin *
- docker port
- docker ps
- docker pull
- docker push
- docker rename
- docker restart
- docker rm
- docker rmi
- docker run
- docker save
- docker search
- docker secret *
- docker service *
- docker stack *
- docker start
- docker stats
- docker stop
- docker swarm *
- docker system *
- docker tag
- docker top
- docker unpause
- docker update
- docker version
- docker volume *
- docker wait
- Engine API
- User Guide
- Docker Compose
- Overview of Docker Compose
- Install Compose
- Getting Started
- Docker Stacks and Distributed Application Bundles
- Using Compose with Swarm
- Quickstart: Compose and Django
- Quickstart: Compose and Rails
- Quickstart: Compose and WordPress
- Environment file
- Environment variables in Compose
- Extending Services in Compose
- Networking in Compose
- Using Compose in Production
- Compose File Reference
- Command-line Reference
- Command-line Completion
- Link Environment Variables
- Controlling startup order
- Frequently Asked Questions
- CS Docker Engine
- Docker Datacenter
- Deploy Datacenter on AWS
- Deploy Datacenter on Linux
- Universal Control Plane 2.0
- Docker Trusted Registry 2.1
- Previous versions
- Universal Control Plane 1.0
- Docker Trusted Registry 2.0
- Docker Cloud
- About Docker Cloud
- Docker Cloud Settings and Docker ID
- Organizations and Teams
- Getting Started
- Introducing Docker Cloud
- Link to your Infrastructure
- Deploy your first node
- Deploy your first service
- Deploy an application
- Introduction to Deploying an app in Docker Cloud
- Set up your environment
- Prepare the application
- Push the image to Docker Cloud's Registry
- Deploy the app as a Docker Cloud service
- Define environment variables
- Scale the service
- View service logs
- Load-balance the service
- Provision a data backend for the service
- Stackfiles for your service
- Data management with Volumes
- Manage Applications
- Add a Deploy to Docker Cloud button
- Automatic container destroy
- Automatic container restart
- Automatic service redeploy
- Create a proxy or load balancer
- Deployment tags
- Manage service stacks
- Publish and expose service or container ports
- Redeploy running services
- Scale your service
- Service API Roles
- Service discovery and links
- Stack YAML reference
- Use triggers
- Work with data volumes
- Manage Builds and Images
- Manage Infrastructure
- Infrastructure Overview
- Container distribution strategies
- Link to Amazon Web Services hosts
- Link to DigitalOcean hosts
- Link to Microsoft Azure hosts
- Link to Packet hosts
- Link to SoftLayer hosts
- SSH into a Docker Cloud-managed node
- Upgrade Docker Engine on a node
- Use the Docker Cloud Agent
- Using Docker Cloud and Packet.net
- Using Docker Cloud on AWS
- Docker Cloud notifications in Slack
- The Docker Cloud CLI
- Known Issues in Docker Cloud
- API reference
- Release Notes
- Docker Hub
- Docker Machine
- Docker Store
- Component Projects
- Docker Swarm
- Swarm Overview
- How to get Swarm
- Evaluate Swarm in a sandbox
- Plan for Swarm in production
- Build a Swarm cluster for production
- Try Swarm at scale
- High availability in Swarm
- Swarm and container networks
- Discovery
- Provision with Machine
- Scheduling
- Overview Docker Swarm with TLS
- Configure Docker Swarm for TLS
- Command line reference
- API response codes
- Docker Swarm API
- Docker Registry
- Registry Overview
- Understanding the Registry
- Deploying a registry server
- Configuring a registry
- Working with notifications
- Recipes
- Reference
- Reference Overview
- HTTP API V2
- Image Manifest V 2, Schema 1
- Image Manifest V 2, Schema 2
- Garbage Collection
- Testing an insecure registry
- Deprecated Features
- Compatibility
- Docker Registry Token Authentication
- Token Authentication Implementation
- Oauth2 Token Authentication
- Token Scope Documentation
- Token Authentication Specification
- Storage Drivers
- Getting help
- Docker Notary
- Docker Swarm
- Open Source at Docker
- Quickstart contribution
- Set up for Engine Development
- FAQ for contributors
- Where to chat or get help
- Style guide for Docker documentation
- About
- Docs archive
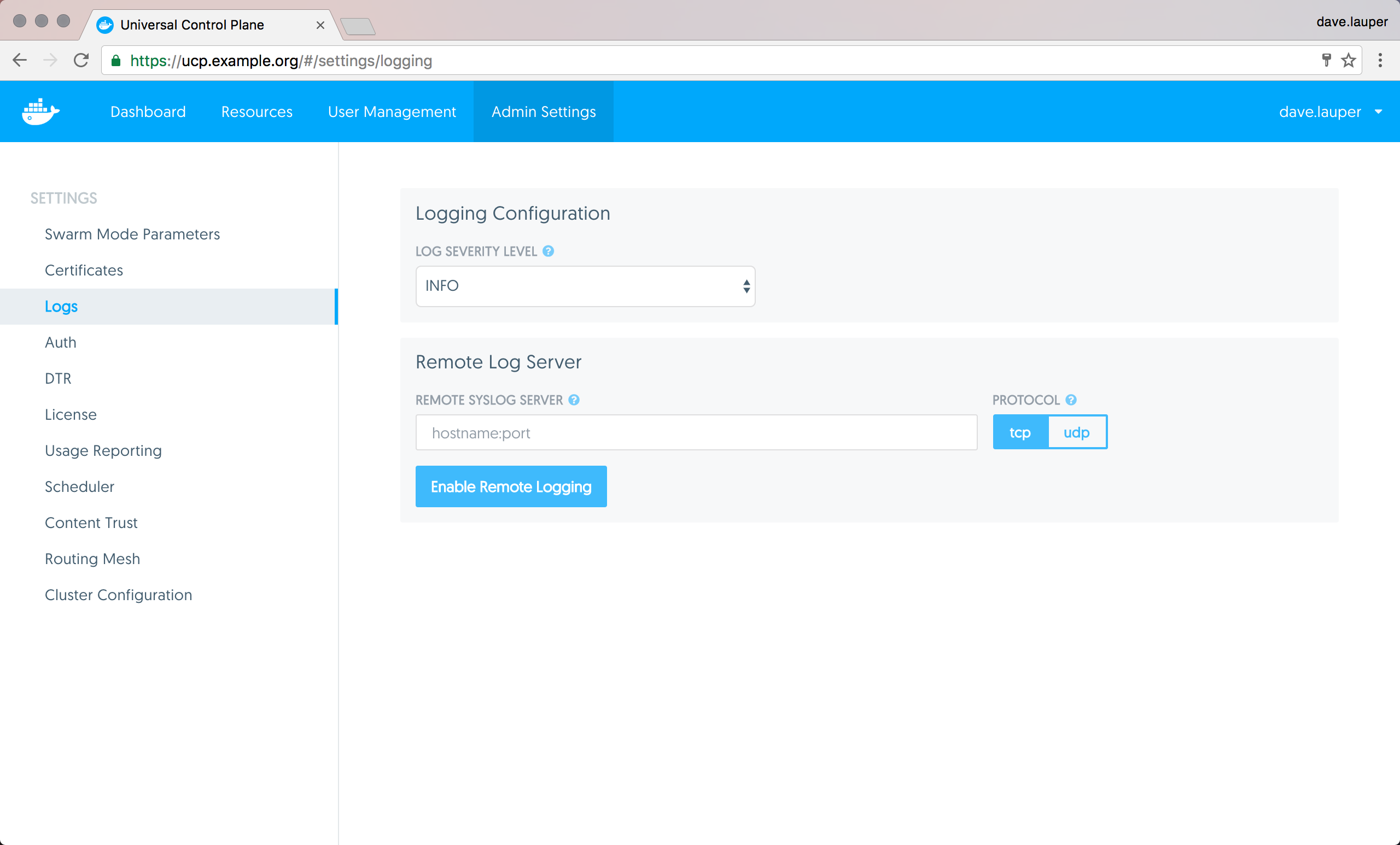
Configure UCP logging
Estimated reading time: 1 minuteConfigure UCP logging
You can configure UCP for sending logs to a remote logging service:
- Login into UCP with an administrator account
- Navigate to the Settings page
- Set the information about your logging server, and click Enable Remote Logging
Example: Setting up an ELK stack
One popular logging stack is composed of Elasticsearch, Logstash and Kibana. The following example demonstrates how to set up an example deployment which can be used for logging.
docker volume create --name orca-elasticsearch-data
docker run -d \
--name elasticsearch \
-v orca-elasticsearch-data:/usr/share/elasticsearch/data \
elasticsearch elasticsearch -Des.network.host=0.0.0.0
docker run -d \
-p 514:514 \
--name logstash \
--link elasticsearch:es \
logstash \
sh -c "logstash -e 'input { syslog { } } output { stdout { } elasticsearch { hosts => [ \"es\" ] } } filter { json { source => \"message\" } }'"
docker run -d \
--name kibana \
--link elasticsearch:elasticsearch \
-p 5601:5601 \
kibana
Once you have these containers running, configure UCP to send logs to the IP of the Logstash container. You can then browse to port 5601 on the system running Kibana and browse log/event entries. You should specify the “time” field for indexing.
When deployed in a production environment, you should secure your ELK stack. UCP does not do this itself, but there are a number of 3rd party options that can accomplish this (e.g. Shield plug-in for Kibana)
Where to go next
 Feedback? Suggestions? Can't find something in the docs?
Feedback? Suggestions? Can't find something in the docs?Edit this page ● Request docs changes ● Get support
Rate this page: